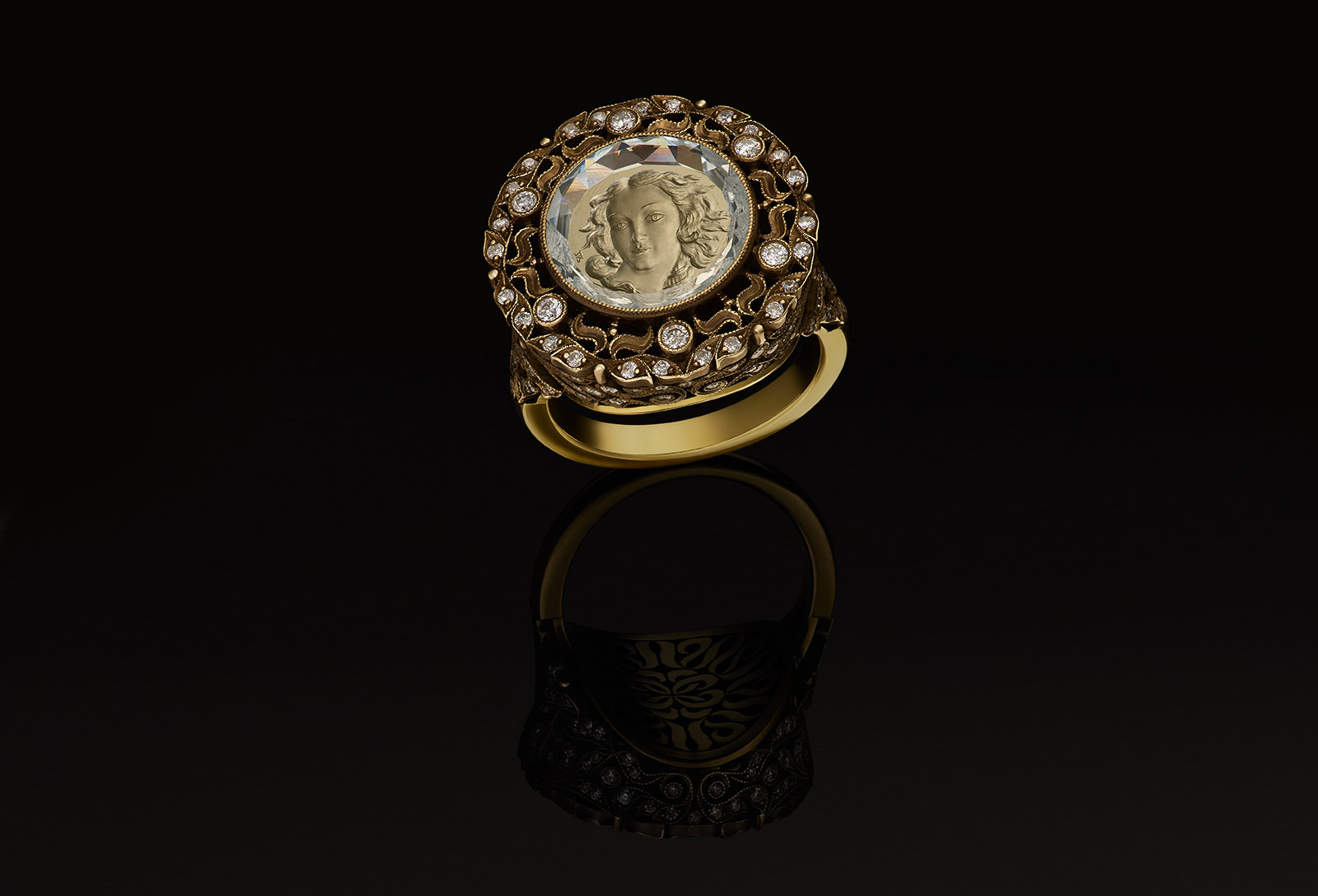

Know Your Jewels: 10 interesting facts about Intaglio gemstones
When searching for inspiration, jewellers may turn their focus to centuries-old practices, meaning that they can become specialists in almost extinct creative techniques. One such devotee of ancient jewellery making skills is ARGENTOV jewellery founder Yaroslav Argentov, a specialist in creating intaglio jewellery. Argentov’s knowledge of this exquisite sub-set of gemstone cutting is extensive; this is an art form which is rarely practised in the modern world, and therefore is already the preserve of museum exhibitions, auctions and collectors’ cabinets. One-of-a-kind, handmade jewellery with intaglios are now an incredibly rare sight to happen upon.
Today I want to share the resurgence of this classic jewellery-making practice and gemstone cutting method by sharing with you 10 interesting facts about intaglio which I discovered when I spoke to Yaroslav Argentov. First and foremost, Argentov drew my attention to the fact that engraving gemstones was one of the very first methods applied to working with precious minerals, and was adopted long before the modern methods of stonecutting were developed. Centuries ago, the earliest craftsmen relied on carving, engraving and intaglio, as they strived to create artistic expression and garner greater value from common and unspectacular gemstones.
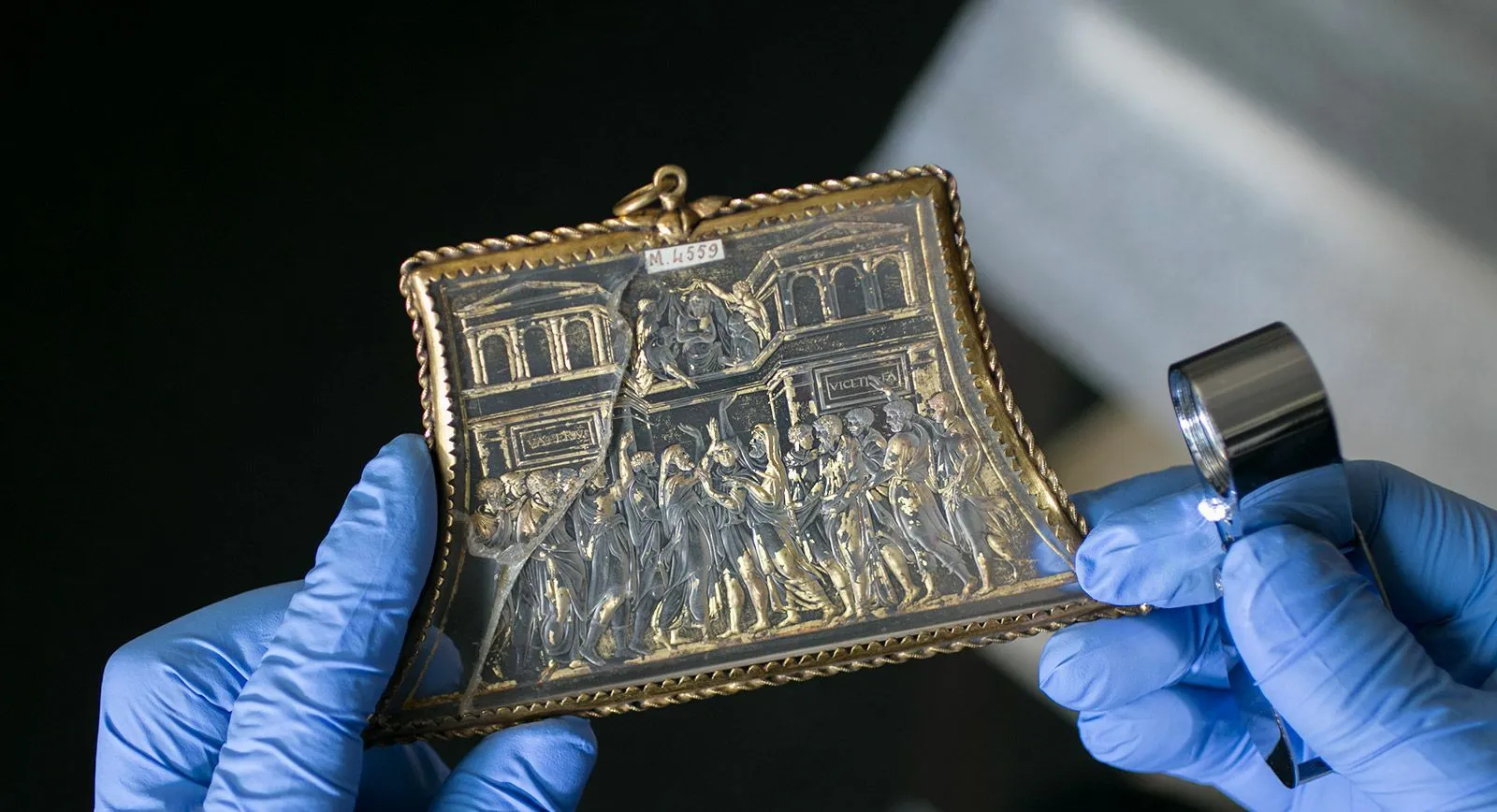
One of the most widely known styles of engraving is in relief, and is known as cameo. It’s contrasting alternative, the cavo-rilievo technique used on precious and semi-precious stones known as intaglio, is less frequently encountered. This is in part due to fact that this kind of carving is not only a specialised skill, but also a highly laborious technique, and the craftsmen who have achieved perfection in their intaglio work are few and far between.
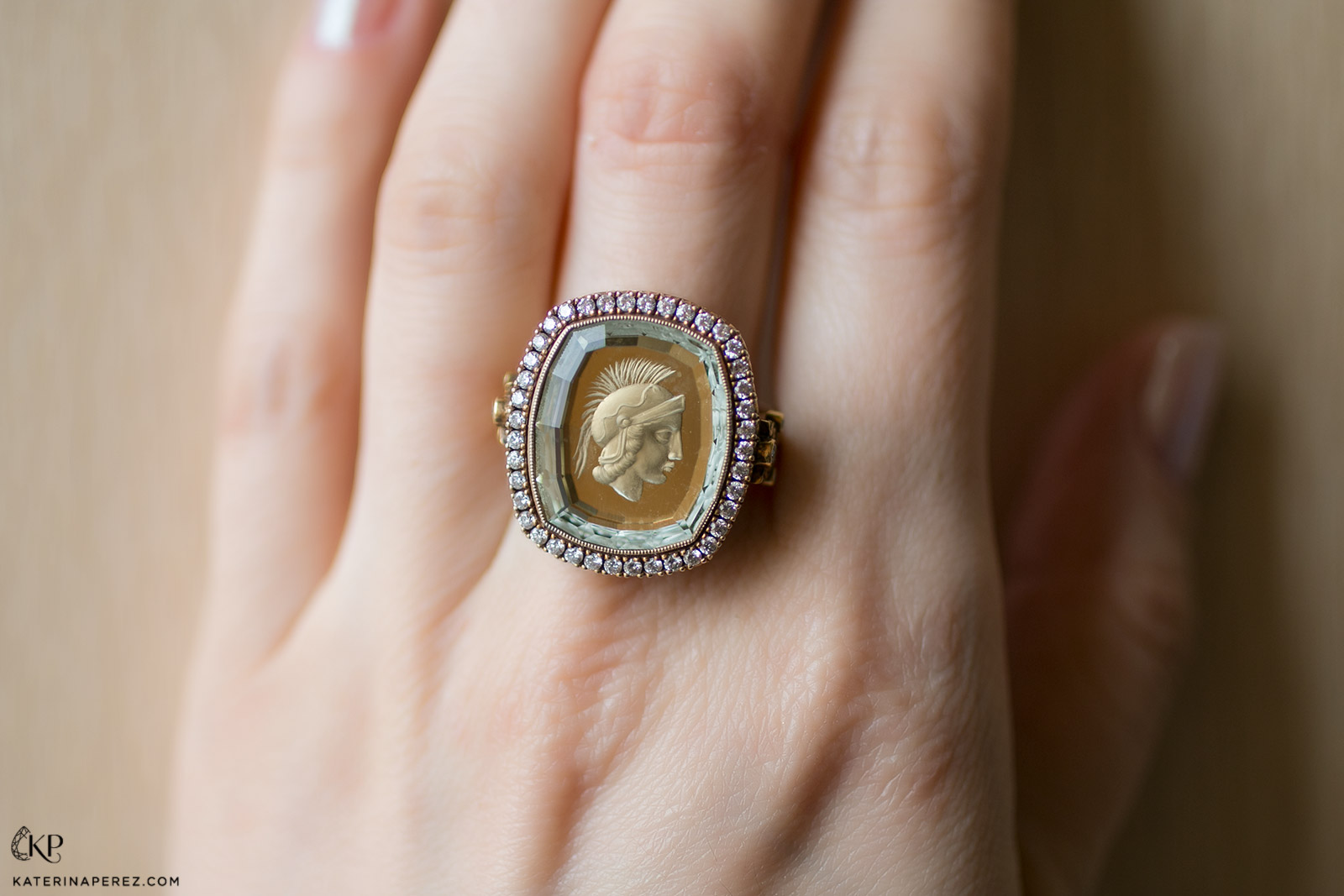

Argentov ring with intaglio
During my discussion with Yaroslav, I was introduced to several interesting facts on the art of intaglio:
1. Intaglio designs surfaced earlier than the more widely recognised cameo, their initial appearance lost in the depths of time. The first traceable evidence of intaglio is when the technique emerged as fairly well-developed in the East in the 4th-3rd centuries B.C. Thereafter, the spread of intaglio pieces widened throughout the ancient world.
2. The optical and electromagnetic properties of gemstones spotted by those living in ancient civilisations engendered a belief in their supernatural powers. As a result, gemstone intaglios were made into amulets. People started to carve distinctive symbols and images onto them, believing that this would improve their chances of success and happiness.
“Jeune bacchant” intaglio by Giovanni Pichler, Rome, 2nd part of the 18th century. From the collection of the National Library of France
3. As property and ownership developed, jewels were used as the personal stamps of their owners; the impression of a gemstone in wax or clay replaced a signature. Eloquent inscriptions that remain attest to this – on one gem in the 6th century B.C., we read: “I belong to Hermotin.”Another states: “I am the seal of Tersis, be careful not to break me!”
4. A seal in ancient times was applied not only to letters, wills and official documents, but also to chests and boxes containing valuables, amphorae of wine and oil, and if we are to believe the comic playwright Aristophanes, jealous husbands would even stamp their seal on the doors to the gynaecea (women’s quarters)!
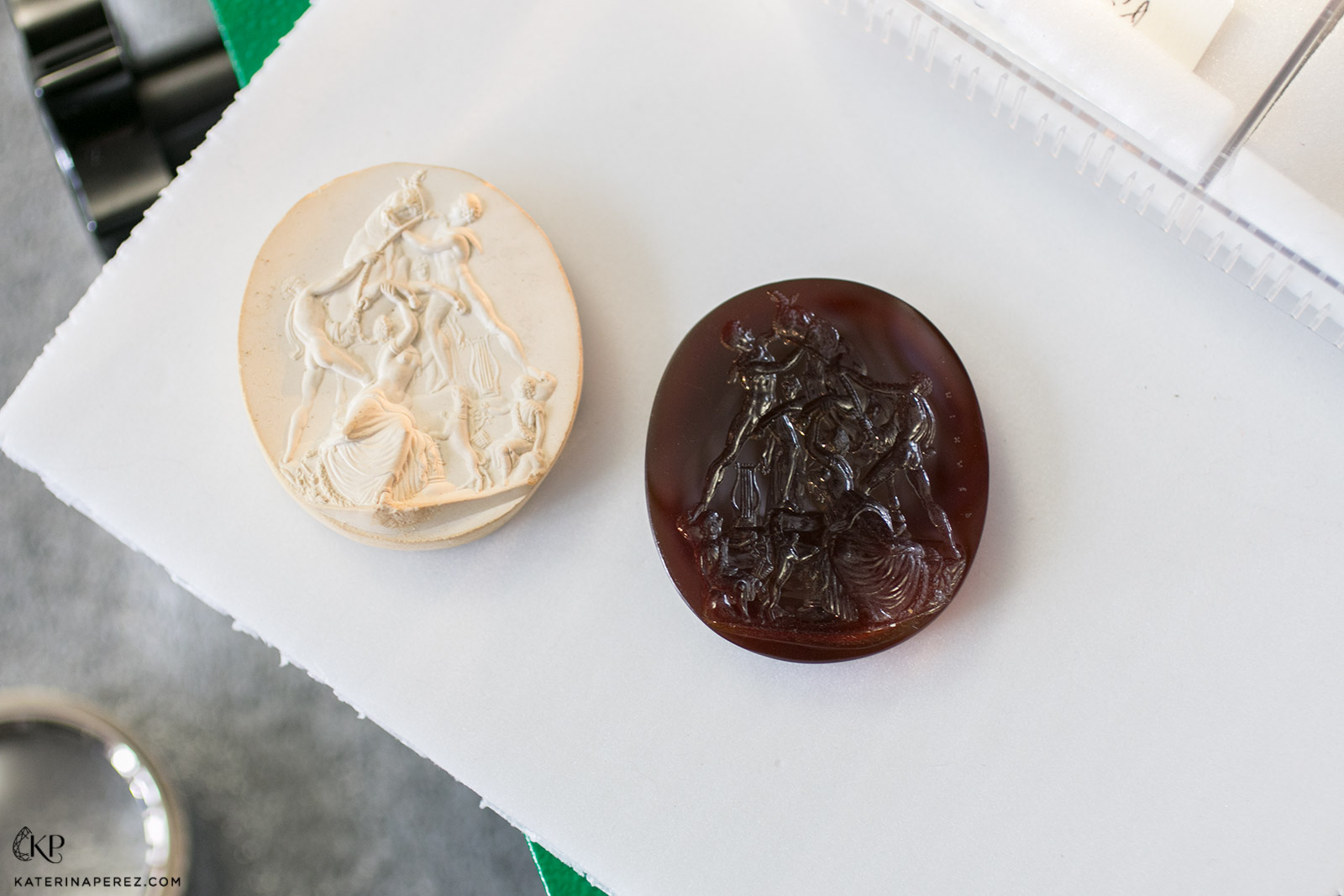

“Groupe du Taureau Farnèse” cornelian intaglio by Louis Pichler. From the collection of the National Library of France
5. Empress Catherine II – commonly known as Catherine the Great – was one of history’s most avid gemstone collectors. She called her passion a “gem disease as contagious as scabies,” acquiring individual gemstones found in Pompei, as well as entire collections, such as a selection of jewels that belonged to the Duke of Orléans. What’s more, for her the value of a piece was entirely vested in the carved gemstones themselves- she would readily ‘demolish’ jewellery, chalices, and furniture so as to re-set and fully enjoy the potential of the intaglio gemstones which they contained. Consequently, her gemstone collection survives in the form of gems which have been mounted into classical settings.
6. Reigning monarchs were not the only ones attracted to collecting intaglio pieces but also aristocrats, scientists and artists. Those who did not have the means to buy originals could instead collect their cast replicas. This is how the artist Goethe could afford to have his own collection of antique intaglio works that were replicas but, nevertheless, considered by him to be one of his most prized possessions.
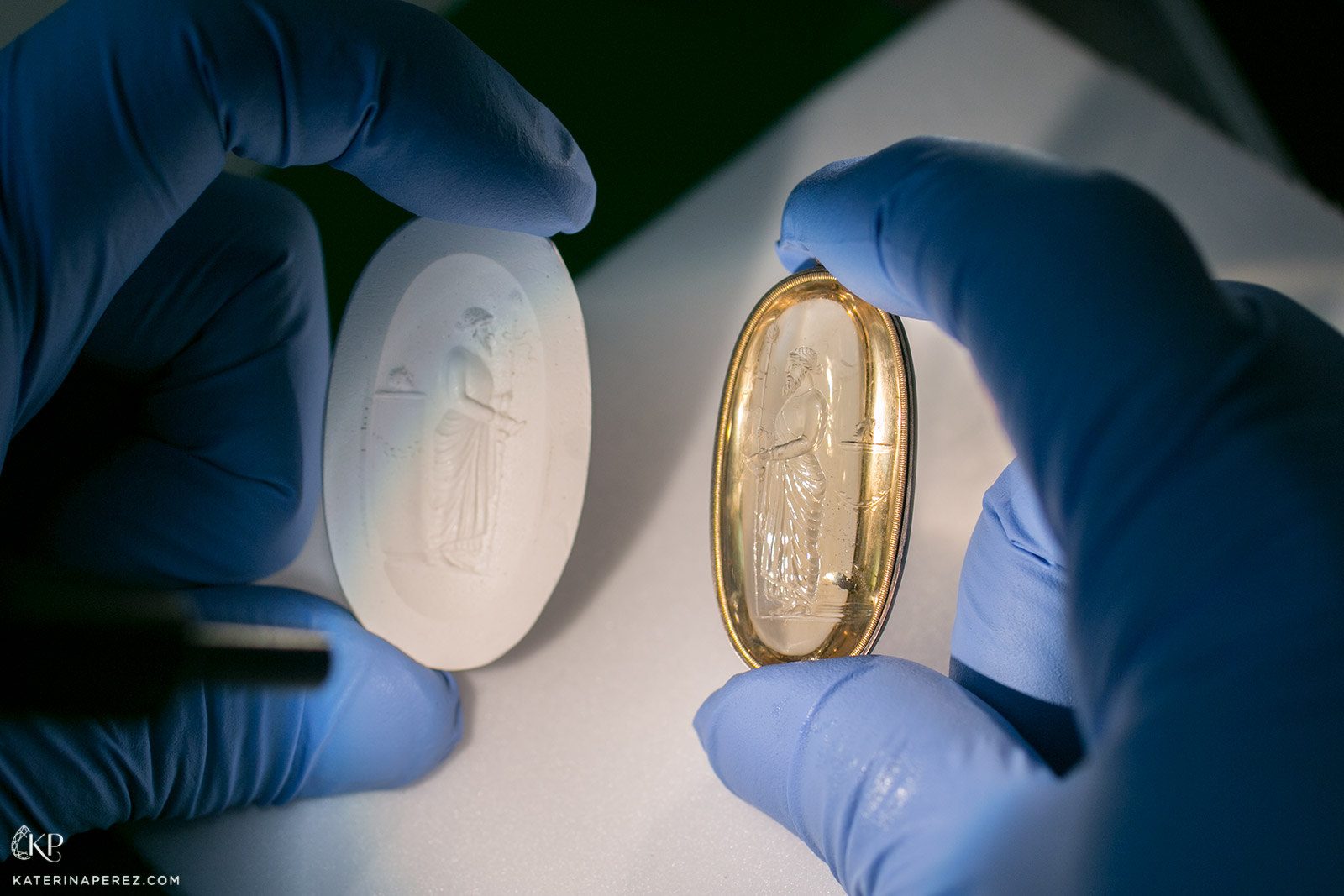

Roman intaglio ‘Dionysos’ carved on citrine. From the collection of the National Library of France
7. Today, the biggest collection of gemstones in the world is in the Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg, Russia – across the variety of displays, there are roughly 20,000 pieces.
8. The technology behind cutting precious stones has not changed substantively for many centuries, except that electrical propulsion and optical tools are now employed. Previously, all of this was done by hand, and required both imagination and unbelievable patience.
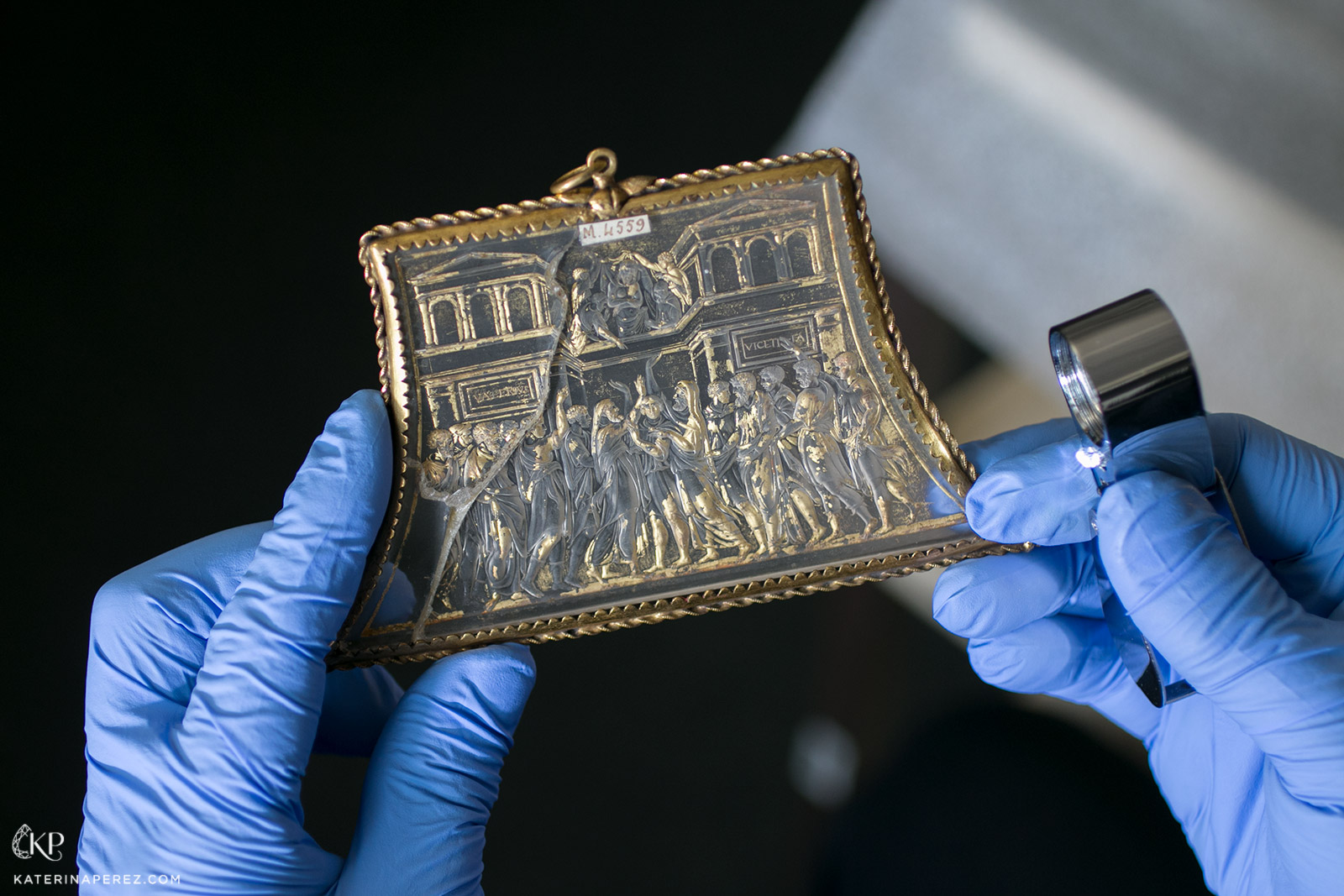

“Ecce homo” intaglio by Valerio Belli created in the 1st part of 16th century. From the collection of the National Library of France
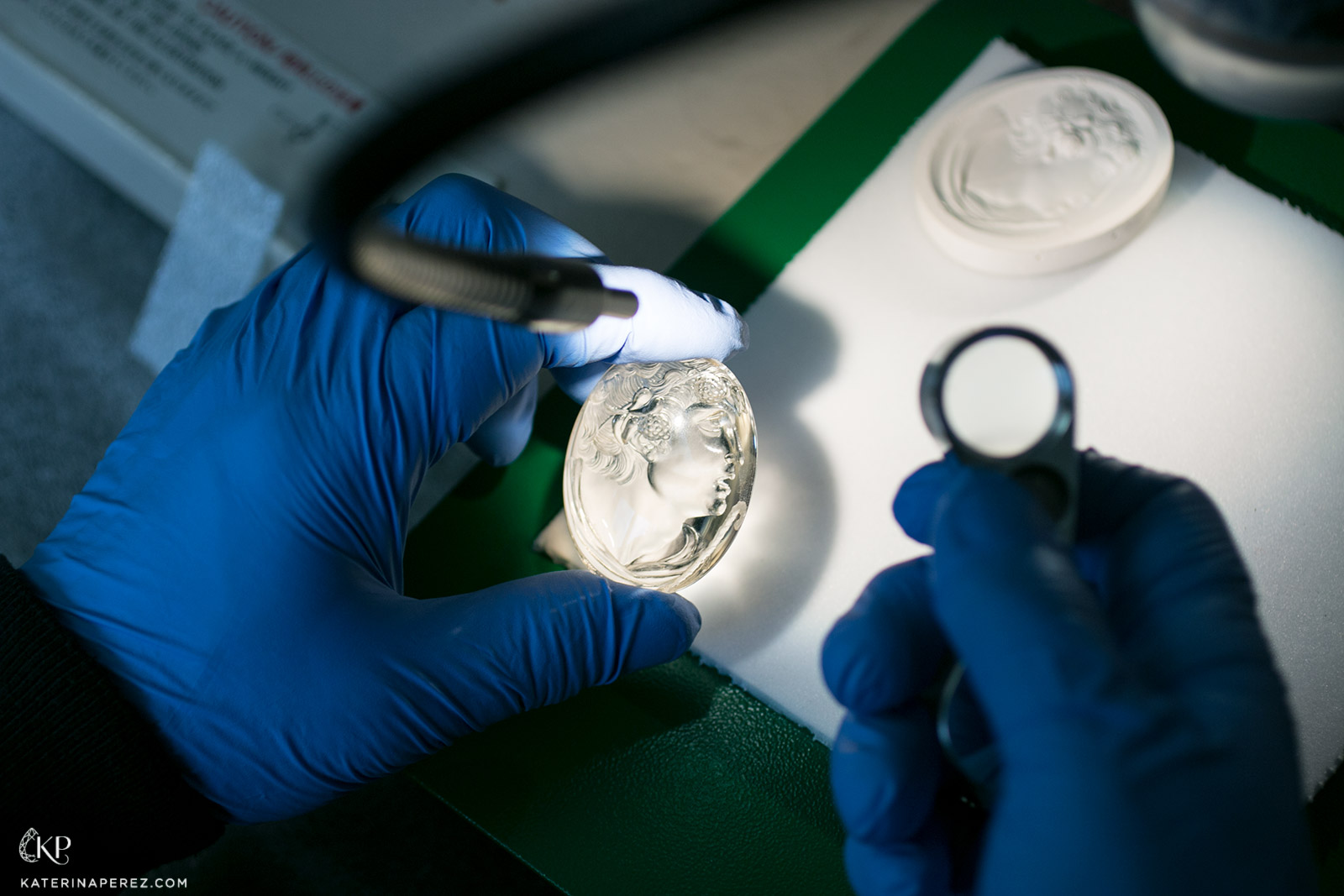
9. The difficulty of creating intaglio lies in the fact that much of the work has to be done practically blind, because the surface of the gemstone is hidden as you cut it – blurred with oil and water. The workman periodically cleans the surface of the stone and makes trial impressions and – as the picture is drawn – it is the mirror image which has to be constantly considered.
10. Intaglios are rather difficult to evaluate consistently. A lot of different parameters have to be taken into consideration: including the skill required to achieve the design and execution, the reputation of the artist and – of course – the cost of the stone.
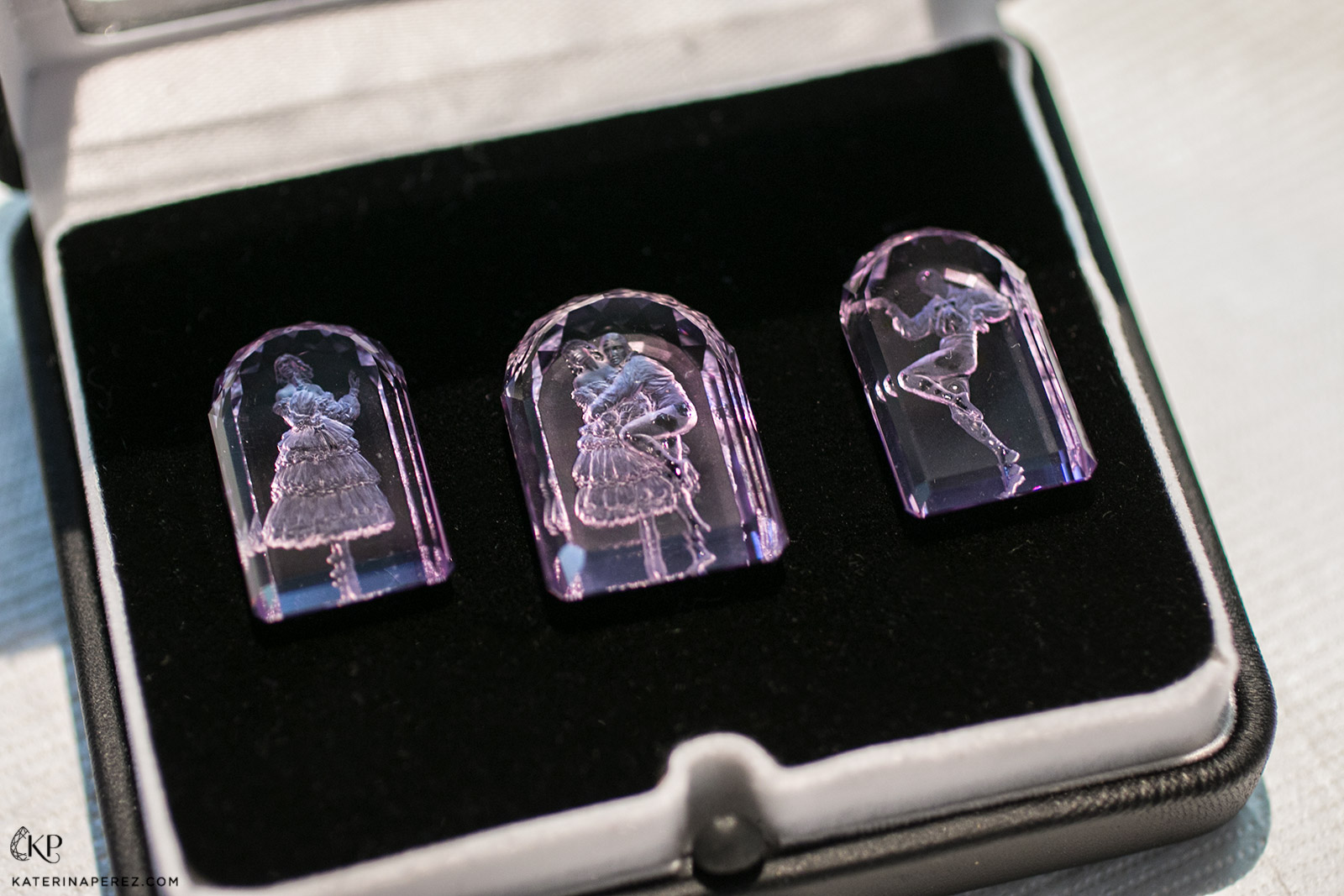

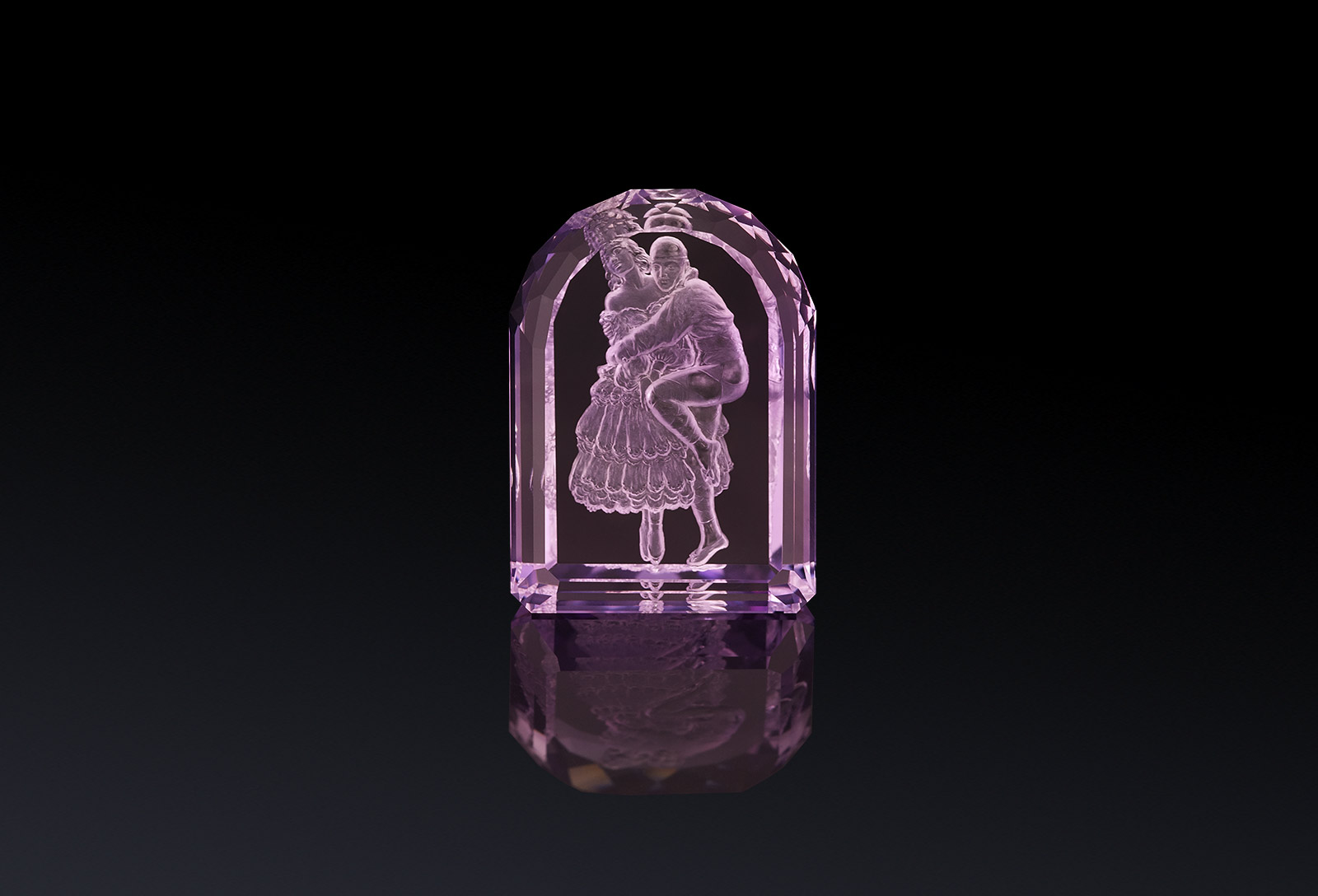
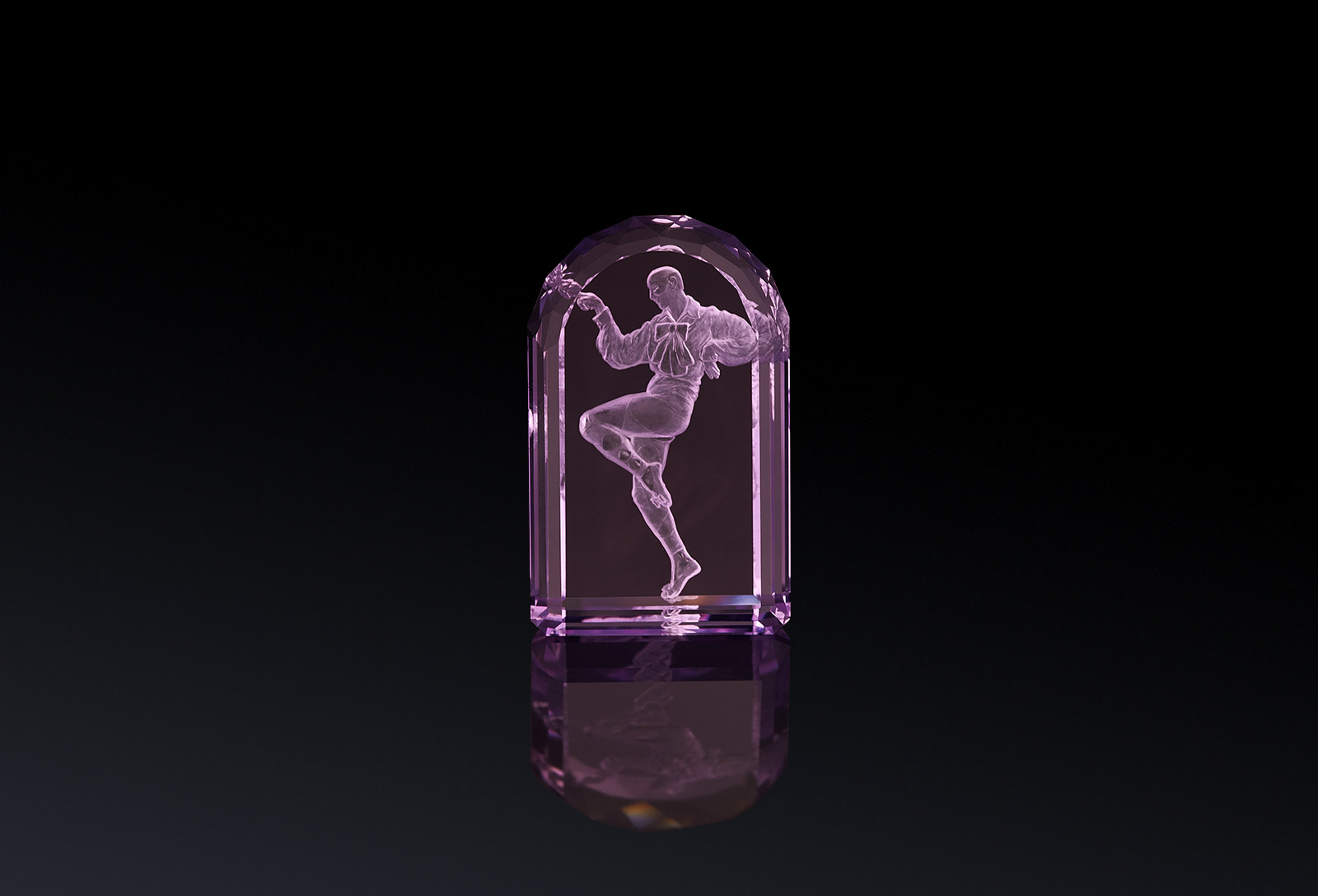
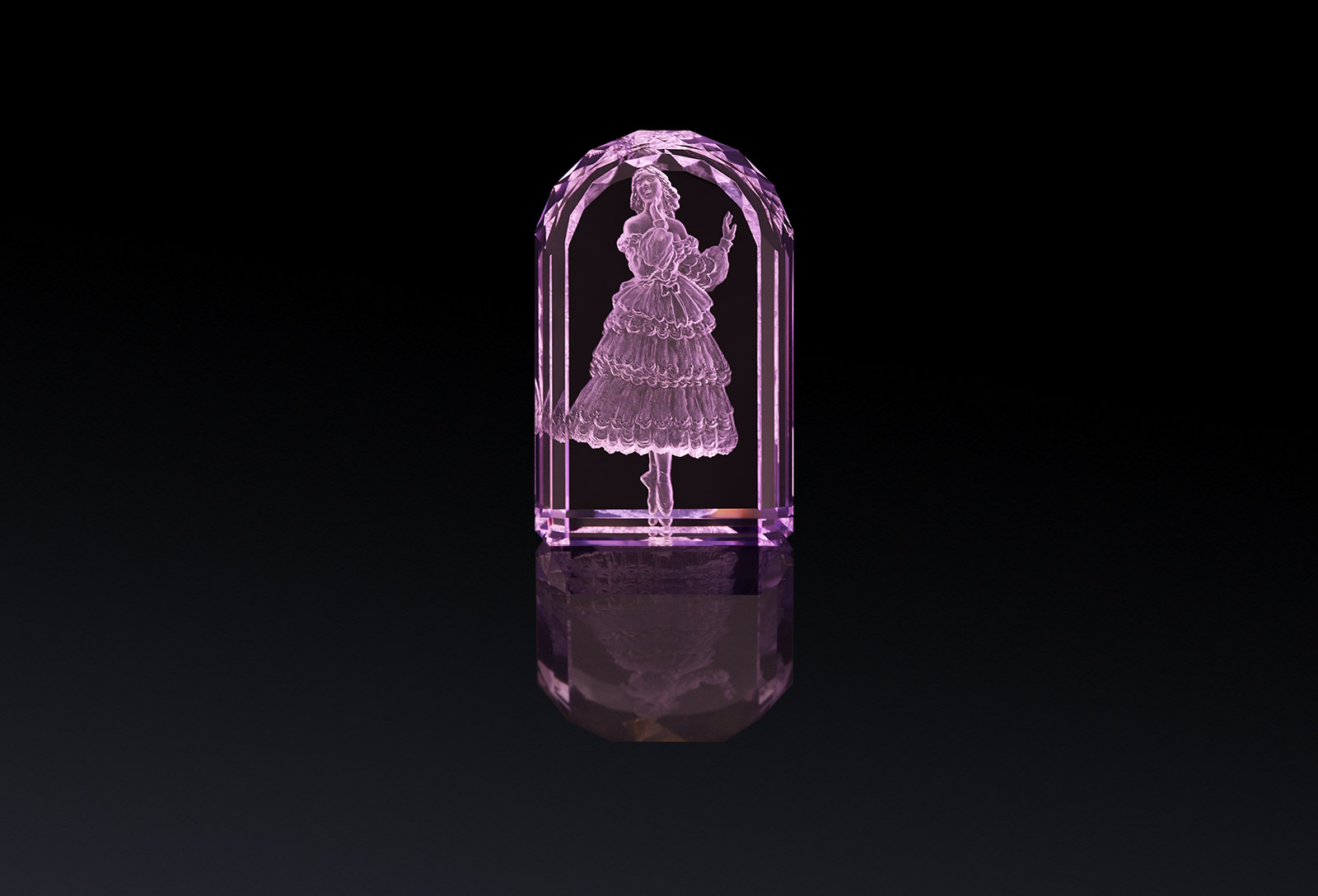
Argentov amethyst intaglios from the ballet series hand carved by Vladimir Popovitch
Alongside Yaroslav Argentov, I was fortunate enough to be shown a selection of centuries old intaglio gemstones when I visited a private gem vault in Paris. The objets d’art that I viewed there have not only stood the test of time, but they have preserved the incredible workmanship and artistry passed down through generations of craftsmen. The impression which these intaglio gems left upon me will last for a lifetime!

WORDS
Katerina Perez is a jewellery insider, journalist and brand consultant with more than 15 years’ experience in the jewellery sector. Paris-based, Katerina has worked as a freelance journalist and content editor since 2011, writing articles for international publications. To share her jewellery knowledge and expertise, Katerina founded this website and launched her @katerina_perez Instagram in 2013.












